
To get a web app from an idea in your head to a real, working product, you need a plan. A proper roadmap that covers everything from the first conversation to what happens after launch. This isn't just about writing code; it's a structured process of defining goals, picking the right tools, designing something people can actually use, and getting it all live without any drama. This roadmap is what keeps your project on track, on budget, and on schedule.
Your Web App Development Roadmap
Building a web app can feel like a mammoth task, but if you break it down into clear, manageable phases, the whole journey becomes much smoother. Don't think of it as one giant project. Instead, see it as a series of connected steps, where each one builds logically on the last.
This structured approach is your best defence against scope creep, keeps costs under control, and ultimately leads to a much better final product that genuinely meets what your users need. The demand for well-built applications is always growing. In fact, the UK's web design services market is projected to hit £658.2 million in 2025, which shows just how crucial professional development is for businesses today. Discover more insights from the IBISWorld report.
The Core Development Lifecycle
The journey from a concept to a live application almost always follows four key stages: definition, design, development, and deployment.
- Define: This is the discovery phase. It’s where you get crystal clear on the app's real purpose, figure out who you're building it for, and list the absolute must-have features.
- Design: Next up, you map out the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) with wireframes and mockups, focusing on making everything feel intuitive.
- Develop: With a solid blueprint in hand, the coding begins. This stage is all about writing the frontend and backend code that brings the design to life.
- Deploy: Finally, you launch the app on a hosting server so people can actually use it, and you put a plan in place for ongoing maintenance.
This infographic gives you a great visual overview of the standard process for bringing a web application from idea to reality.
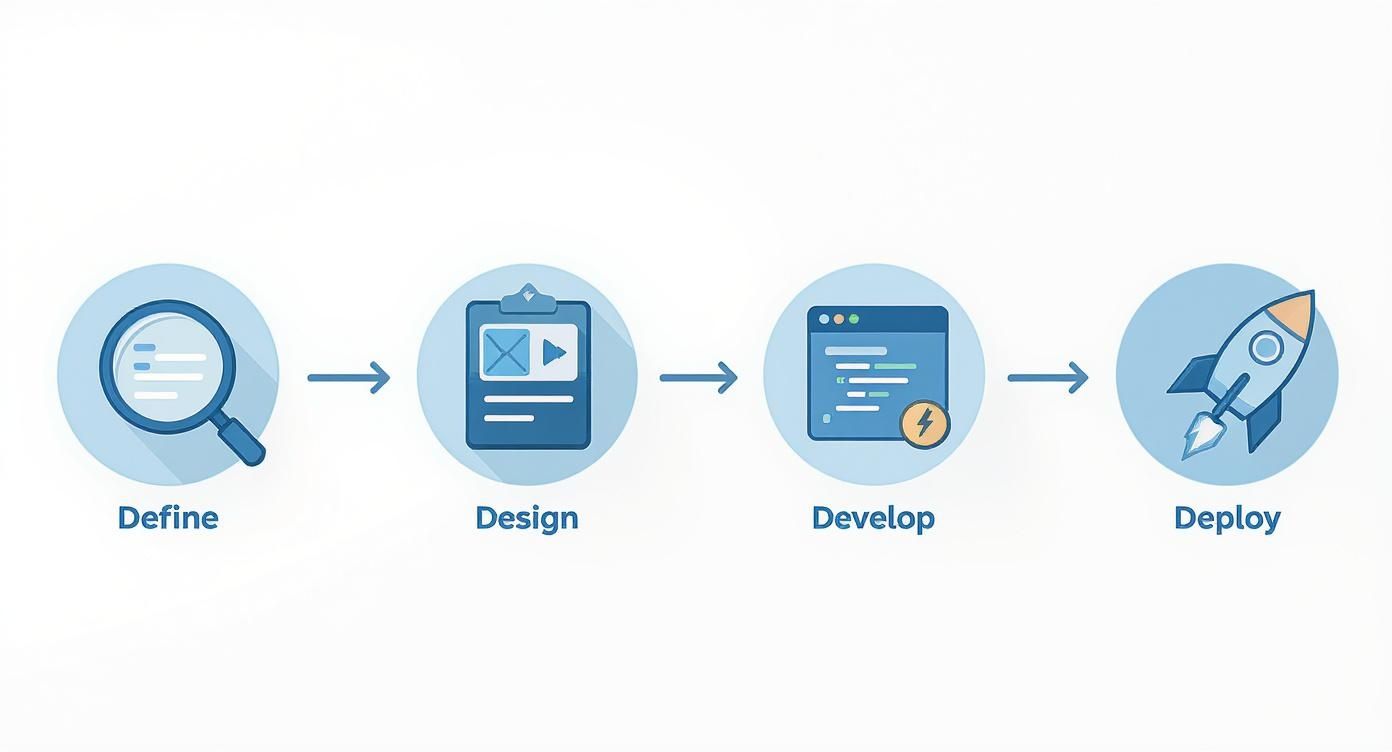
This visual roadmap makes it clear that successful development is a sequential process. Understanding this lifecycle is the first step towards building a product that not only works but lasts. You can learn more about the intricacies of this journey in our complete guide to web application development.
To give you a clearer idea of the timeline, here's a quick look at how these phases typically break down.
Web App Development Phases at a Glance
| Phase | Typical Duration | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery & Definition | 1-3 Weeks | Defining goals, user personas, technical requirements, and core features. |
| Design & Prototyping | 2-4 Weeks | Creating wireframes, mockups, and interactive prototypes for UX/UI. |
| Development | 4-12+ Weeks | Writing frontend and backend code, building the database, and integrating APIs. |
| Testing & QA | 2-4 Weeks | Performing unit, integration, and user acceptance testing to find and fix bugs. |
| Deployment & Launch | 1 Week | Setting up hosting, configuring the server, and making the application live. |
| Maintenance & Support | Ongoing | Monitoring performance, fixing bugs, and planning future feature updates. |
Of course, these timelines are just a guide. The real duration depends entirely on the complexity of your project, but this table gives you a solid framework for what to expect.
Building Your Foundation With Solid Discovery
Jumping straight into code without a clear plan is tempting, but it’s a gamble. You might shave off a few days on the timeline yet end up with expensive rewrites and a product that never finds its audience. That first deep-dive into discovery turns a sketch into a solid blueprint.
In this phase, you pin down what success looks like. Pull everyone—stakeholders, designers, developers—into the same conversation. Start by uncovering the core business objectives that will steer every decision.
Clarifying Business Objectives
Before a single function is built, ask why the web app needs to exist. Do you want to boost online sales, reduce manual workloads, or deepen customer engagement? Clarity here keeps every team member pulling in the same direction.
Try structured interviews with project sponsors. Extract the true motivations behind the idea.
- Define Success Metrics: Which KPIs will prove you’ve hit the mark? Daily active users, a drop in support tickets, or a direct revenue uplift?
- Identify Core Problems: What exact pain point must the app solve? Aim for tangible figures—for example, trimming 10 hours of admin work each week.
- Establish a Budget and Timeline: Nail down the financial and time constraints so you don’t chase features you can’t afford.
Assuming everyone sees the goal the same way is a common pitfall. Document your objectives and turn them into a north star that prevents scope creep.
This documented vision ensures you build features that actually matter.
Understanding Your Users
Once business aims are clear, switch your gaze to those who will use the app every day. “Users” need a real persona, not a vague demographic.
Gather straight-from-the-source feedback. In Midlothian retail, that might mean sitting down with 20 regular customers to explore their browsing habits and pain points.
- Build User Personas: Sketch out semi-fictional characters—like Fiona, a 45-year-old store owner in Dalkeith focused on easy booking management.
- Map User Journeys: Draw the steps each persona takes—from logging in to completing a purchase. Spot where frustration could spring up and smooth it out.
This evidence-driven research keeps you honest and user-focused throughout the build.
Defining Functional And Non-Functional Requirements
With business and user insights in hand, it’s time to turn those ideas into precise specs. Your developers need both what and how.
Functional requirements spell out the app’s must-have features: user authentication, payment gateways, search filters—every detail counts.
Non-functional requirements describe performance and quality:
- Performance: Pages should render in under 2 seconds.
- Security: Full compliance with UK GDPR regulations.
- Scalability: Support peaks of 1,000 concurrent users seamlessly.
- Accessibility: Meet WCAG 2.1 AA standards.
Documenting these requirements—and weaving them into your web design processes—creates a roadmap everyone can follow.
Choosing the Right Tech Stack and Architecture
Right, with the discovery phase done and dusted, your abstract ideas need to be turned into concrete technology. Choosing your tech stack isn't about jumping on the latest bandwagon; it’s a strategic call. You're balancing what the project needs, what your team already knows, and how you plan to scale and maintain this thing in the long run.
Getting this right is fundamental. It's the difference between building a robust, efficient app and creating a technical headache for yourself down the line. This is where you break the application down into its core layers—the frontend, the backend, and the database—and pick the best tools for each job. These pieces have to work together perfectly to deliver the user experience you’ve so carefully planned out.
This is the logo for React, a hugely popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces. Maintained by Meta, its component-based approach has made it a go-to for creating complex, interactive web applications for a reason.
Navigating Frontend Frameworks
The frontend is what your users actually see and touch, making it a critical piece of the puzzle. The JavaScript framework you choose will heavily influence the development experience and, more importantly, your app's performance.
Here’s a quick rundown of the main players:
- React: Known for its enormous ecosystem and component-based structure, React is fantastic for building complex, dynamic user interfaces. Its massive community means finding support or skilled developers is generally much easier.
- Vue.js: Often praised for its gentle learning curve and brilliant documentation, Vue.js is a progressive framework that’s incredibly easy to pick up. It's a superb choice for small to medium-sized projects where you need to move quickly.
- Angular: A comprehensive, "opinionated" framework from Google, Angular provides a complete, structured solution for building large-scale applications. It's ideal for enterprise-level projects that demand consistency and long-term maintainability.
Honestly, your team's existing expertise is often the deciding factor here. A team that's already proficient in one framework will deliver faster and with higher quality than a team learning a new one from scratch.
To help you see the wood for the trees, here's a quick comparison of the leading frameworks.
Comparing Popular Frontend Frameworks
A practical look at the key differences between the leading JavaScript frameworks to help you decide.
| Framework | Learning Curve | Performance | Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|---|
| React | Moderate | High (uses a virtual DOM for efficient updates) | Massive (huge library of components and tools) |
| Vue.js | Low | Excellent (very lightweight and fast) | Growing rapidly, very flexible |
| Angular | High | Good (can be bulky but is very powerful) | Comprehensive (everything you need is built-in) |
Ultimately, the best choice hangs on your specific needs. Think about the complexity of your UI, your performance targets, and your long-term vision. We explore this in more detail in our guide to web and application development.
Selecting a Backend and Database
The backend is the engine room of your web app. It handles all the business logic, crunches the data, and talks to the database. Your choices here will directly impact scalability, performance, and even your hosting costs.
Common backend technologies include Node.js, which is known for its speed and for using JavaScript (letting you use one language across the whole stack). Then there's Django, a Python framework famous for its "batteries-included" approach, which offers loads of built-in features that really speed up development.
Your database choice is just as important.
- SQL Databases (like PostgreSQL or MySQL) are your best bet for applications with structured, relational data. Think of an e-commerce store where products, orders, and customers are all neatly interconnected.
- NoSQL Databases (like MongoDB) offer more flexibility and are brilliant for unstructured data or apps that need to scale out very, very quickly.
The Rise of Low-Code Solutions
For some projects, especially internal tools or a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), traditional coding isn't the only way forward. Developing a web application in the UK has become much more accessible thanks to the boom in low-code and no-code platforms. These tools offer visual development environments that can slash your timelines.
In fact, some businesses using these tools have reported a 40% decrease in time-to-market for new web applications.
These platforms are excellent for validating an idea quickly or automating simple business processes without a huge upfront investment in custom development. They empower teams to build functional applications with minimal coding knowledge, freeing up specialist developers to focus on more complex challenges.
Designing a Seamless User Experience
Once your tech stack is locked in, it’s time to shift your focus to the single most important part of any application: the user’s journey. An incredible user experience (UX) is what separates an app people use every day from one they forget a minute after downloading. This is where you turn a list of features into an intuitive and engaging interface.
But the process doesn’t start with picking colours and fonts; it starts with the blueprint. You need a solid structure before you get lost in the visual details. That’s where wireframing comes in.
From Wireframes to Prototypes
The first step is to create low-fidelity wireframes—simple, black-and-white layouts that act as the architectural drawings for your app. Their only job is to map out the information architecture and define user flows without the distraction of branding or design elements.
This is the perfect moment to answer the big questions:
- Where does this button actually lead?
- How does a user get from their dashboard to their account settings?
- Is the main call-to-action crystal clear on every single screen?
Once the basic structure feels solid, you can move on to high-fidelity mockups or interactive prototypes. These are far more detailed and give a much better feel for the final product, letting you test your assumptions with real people. A UK fintech startup famously ran a one-week design sprint using interactive prototypes, uncovering huge navigation problems in their mobile layout before writing a single line of code. It saved them weeks of expensive rework.
Creating a Responsive and Accessible Design
In today's world, people will use your web app on everything from huge desktop monitors to tiny smartphones. A responsive design isn't a "nice-to-have" anymore; it's a non-negotiable requirement. Your app must adapt gracefully to any screen, ensuring a consistent and intuitive experience for everyone.
This means more than just shrinking things down. It involves completely rethinking layouts, optimising touch targets for smaller screens, and making sure performance stays snappy, even on a weak mobile connection. A well-crafted design system, with reusable components and clear guidelines, is the key to achieving this consistency without reinventing the wheel every time. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on how to improve website user experience.
A common mistake is treating accessibility as an afterthought. Designing for inclusivity from the very beginning not only helps users with disabilities but also improves the experience for everyone.
Adhering to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) is essential. This includes practices like:
- Providing text alternatives for all non-text content, such as images.
- Ensuring sufficient colour contrast between text and its background.
- Making all functionality available from a keyboard.
Ultimately, designing a great user experience means thinking inclusively from the start. You can learn more by focusing on creating inclusive designs through web accessibility and user experience. A study by the WebAIM Million project found that a staggering 96.3% of homepages had detectable WCAG 2 failures. This highlights a massive opportunity to stand out simply by building an app that everyone can actually use.
Nailing an Efficient Development Workflow
Moving from a polished design to a fully working application takes more than just talented developers; it demands a solid, repeatable workflow. This process is the engine room of your project. Get it right, and you ensure consistency, catch bugs early, and make collaboration feel effortless. Without it, even the sharpest teams can get bogged down in chaos and miscommunication.
The aim is to create a predictable system for turning ideas into clean, functional code. This means standardising how that code is written, checked, tested, and ultimately released. By putting these processes in place from day one, you’ll slash manual errors, speed up your delivery, and build a much higher-quality app.
Standardising With Version Control
The absolute bedrock of any modern development process is version control, and Git is the undisputed king. Your first practical step is setting up a central code repository on a platform like GitHub or GitLab. This becomes the single source of truth for your entire project.
A clear branching strategy is essential to stop developers from tripping over each other. Many teams swear by a model like GitFlow, which uses different branches for specific jobs:
- Main Branch: This holds the stable, production-ready code that your actual users are interacting with. It’s sacred.
- Develop Branch: This is the integration hub where all completed features are merged together before they’re bundled up for a release.
- Feature Branches: For every new feature or bug fix, a developer creates their own separate branch. This keeps their work isolated until it's finished, tested, and ready for review.
This structured approach prevents people from accidentally overwriting each other’s work and makes it straightforward to manage multiple streams of development at once. It brings a sense of calm to the potential chaos of a growing project.
Automating for Quality and Speed
Manually testing and deploying code is slow, mind-numbingly repetitive, and wide open to human error. This is where a Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline completely changes the game. A CI/CD pipeline automates all the steps needed to get fresh code from a developer’s computer into the hands of your users.
Every time a developer pushes new code, the pipeline can automatically kick off a series of checks. These typically include running automated unit tests to make sure individual functions work as expected, and integration tests to ensure all the different parts of the app play nicely together. For anyone serious about comprehensive testing, especially for complex systems like e-commerce, it's worth understanding the best practices for building an end-to-end automation framework.
A small UK development team, for instance, managed to cut their release cycle time in half simply by integrating automated tests into their pipeline. This simple change caught bugs much earlier, drastically reducing the time spent on manual quality assurance.
If all the tests pass, the code can be merged. The "deployment" part of the pipeline can then automatically push these changes to a staging server for a final check before going live.
Ensuring Consistency With Containerisation
One of the oldest and most frustrating headaches in software development is the classic "well, it works on my machine" problem. An app runs perfectly for one developer but breaks for another, or fails completely in the live environment because of tiny differences in system settings.
Containerisation tools like Docker solve this problem beautifully. Docker lets you package up your web app and all its dependencies—every library, tool, and setting it needs—into a single, isolated "container." This container is a lightweight, standalone package that runs identically, no matter where you put it.
By using containers, you guarantee that your application behaves consistently at every single stage: from a developer's laptop to the testing server and all the way to production. This wipes out a whole category of environment-related bugs and makes the entire deployment process far more reliable.
Launching and Maintaining Your Web App
Getting to the end of the development phase feels like a huge win, but it's not the finish line. Far from it. Moving from building your app to launching it involves a meticulous pre-flight check to make sure everything is stable, secure, and ready for your first users. This final push before going live is what protects your reputation and sets you up for long-term success.
The focus now switches from creating features to trying to break them—in a controlled way, of course. Rigorous testing is completely non-negotiable. It’s your last real chance to catch issues before they affect real people and potentially damage your brand.
The Final Push Before Going Live
Before you even think about hitting the deploy button, your app needs to survive a trial by fire. This means several layers of quality assurance, each designed to scrutinise a different part of the application. Think of it as a comprehensive health check.
- Comprehensive Testing: This isn't just about clicking around. It covers unit tests for individual functions, integration tests to ensure different modules play nicely together, and end-to-end tests that simulate complete user journeys from start to finish.
- Performance and Load Testing: How does the app hold up under pressure? Simulating high traffic helps you spot bottlenecks and ensures your app won’t crumble during peak hours. It's a common problem that affects over 75% of web apps during unexpected traffic spikes.
- Security Audits: This is absolutely critical. Run automated vulnerability scans and, if the budget allows, get manual penetration tests done to find and patch security holes before they can be exploited by someone with bad intentions.
Once you’re confident that the app is solid, it’s time to decide where it’s going to live.
Choosing Your Hosting and Deployment Strategy
Your hosting provider is the foundation your web app will run on. The right choice really depends on your technical needs, your budget, and how much you expect to grow in the future.
Modern platforms like Vercel or Netlify are brilliant for frontend-heavy applications, offering seamless deployment straight from your Git repository. For more complex backends, the cloud giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud Platform provide immense power and flexibility, though they definitely come with a steeper learning curve.
Your deployment process should be as automated as possible. A well-configured CI/CD pipeline ensures that every update is tested and deployed consistently, minimising the risk of human error and making your release cycle faster and more reliable.
With your app live, your job has only just begun. The post-launch phase is all about observation and upkeep.
Post-Launch Monitoring and Upkeep
Once your web app is out in the wild, you need to know what’s happening under the bonnet at all times. This is where monitoring and analytics tools become your best friends.
Set up application performance monitoring (APM) tools to track things like server response times, error rates, and database queries. This gives you real-time insight into the health of your app, allowing you to spot and fix issues before your users even notice them. On the user-facing side, analytics tools like Google Analytics or the privacy-focused Plausible will tell you how people are actually using your app, providing invaluable data to guide future improvements.
Finally, proactive maintenance is the key to longevity. This isn't something you do when things break; it's a regular, scheduled activity. A solid plan for ongoing support ensures your app remains secure, performs well, and stays up-to-date with evolving tech. You can explore the essentials in our detailed guide to website maintenance and support.
Get a routine sorted for these essentials:
- Regular Backups: Automate daily or weekly backups of your database and all your application files. Don't skip this.
- Security Patches: Keep all your software dependencies and server software updated to protect against new vulnerabilities as they’re discovered.
- Performance Reviews: Every so often, check your app's speed and resource usage to catch any performance degradation over time.
This disciplined approach ensures your web app remains a healthy, valuable asset for your business long after the initial launch buzz has faded.
Common Web App Development Questions
People always have a few key questions when they start thinking about building a web app. Getting clear answers to these early on can save a huge amount of time and money down the line, so let's tackle some of the big ones.
What are the first steps to develop a web app?
Before you even think about code, you need a solid plan. It all starts with a proper discovery phase where you get crystal clear on who the app is for and what problem it solves for them. This initial groundwork guides every single design and technical decision you'll make later.
For example, we saw a Dalkeith-based retailer interview just 20 of their regular customers. The insights they gathered helped them map out genuine user needs and saved them weeks of rework on features nobody actually wanted.
Getting this right means your team has clear, agreed-upon goals before a single line of code is written or a design mockup is approved.
- Define your target audience and sketch out a few user personas.
- Document the absolute must-have features and map out user journeys.
- Set a realistic budget, timeline, and the metrics that will define success.
A well-executed discovery phase can reduce expensive rework by up to 30%. It’s the single most important step.
Choosing Between React And Vue
Picking a frontend framework often comes down to your team's existing skills and how complex your app is going to be.
React is a powerhouse with a massive ecosystem, making it a brilliant choice for complex, large-scale applications. Vue, on the other hand, is known for its gentler learning curve, which can be a huge advantage for smaller teams or projects that need to get moving quickly.
But the decision goes deeper than that. You have to think about long-term maintainability, the strength of the community support, and the availability of plugins you might need later.
| Framework | Best For | Learning Curve |
|---|---|---|
| React | Complex, data-heavy UIs | Moderate |
| Vue | Small to medium projects & rapid prototyping | Low |
If you’re really on the fence, a great approach is to build a small proof-of-concept or a core module in each framework. Getting some hands-on experience before you commit fully can reveal which one feels right for your team and your long-term goals.
Best Way To Deploy A Modern Web App
For reliable and stress-free releases, automated CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) is the industry standard. Using a service like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI to automatically run tests and push updates is a game-changer.
A modern deployment pipeline typically involves a few key stages:
- Automated tests run on every single code commit.
- Containerisation (using something like Docker) ensures a consistent environment from development to production.
- The app is deployed to cloud hosting with easy rollback settings in case something goes wrong.
"Switching to continuous delivery reduced our release failures by 40%," says a lead developer from a UK tech team we know.
A robust pipeline means every code change is thoroughly tested and ready for production, giving you confidence and speed.
How often should I perform app maintenance?
You should plan for regular maintenance at least once a quarter. This is your chance to update dependencies, run security audits, and look for performance optimisations. Of course, any critical security vulnerabilities need to be patched immediately.
Regular check-ins are crucial because they:
- Keep your app compliant with regulations like GDPR.
- Prevent technical debt from piling up and becoming a major problem.
- Improve the user experience with fresh optimisations and bug fixes.
Ready to learn more about how to develop a web app? Get expert help from Altitude Design here: https://altitudedesign.co.uk